No doubt: in recent years, with the growing adoption of telecommuting, flex office, and hybrid work, companies are facing a major challenge: how to optimize the use of their workspace?
In a context where flexibility becomes the norm and where real estate costs weigh heavily on budgets, it is crucial for companies to know the occupancy rate of their spaces and to vigilantly monitor its evolution over the years.
Indeed! Because today, it’s no longer just about providing a space to work, but optimizing every square meter to meet the new expectations of employees (and they are significant), as well as economic imperatives.
In this article, discover the methods and tools for analyzing the occupation of your offices, and see how a small change can make a big difference. Focus!
Let’s go back to basics! What is the occupancy rate? – Definition
The occupancy rate of workspaces is a crucial metric in managing corporate infrastructure, reflecting the efficiency and use of available spaces.
To simplify: it helps to know how full and utilized the offices are.
There are two types of occupancy rates:
- Theoretical occupancy rate: This rate corresponds to the ratio between the number of workstations and the maximum capacity of the building. In other words, it is the number of available desks compared to what the building can accommodate. It expresses an ideal view of the occupancy of the premises, independent of daily variations in presence and use.
- Actual occupancy rate: This measures the number of workstations actually used within the company, compared to the total number of available posts. It provides a more accurate and pragmatic picture of the use of workspaces, taking into account daily fluctuations in occupancy.
These two indicators (theoretical and real) are essential for optimal management of workplaces, allowing the alignment of infrastructure with operational needs and improving organizational efficiency.
How to calculate the occupancy rate of your workplace? 4 very simple steps!
To calculate the occupancy rate of your workplace:
1. Count your available workstations: note the total number of workstations available in your offices.
2. Measure actual usage: over a representative period (such as a week), count how many of these stations are actually occupied each day. For this, you can use a badge system at the entrance of your building, a desk booking application(= workstation reservation), or infrared presence sensors to detect movement when a desk and a meeting room become available.
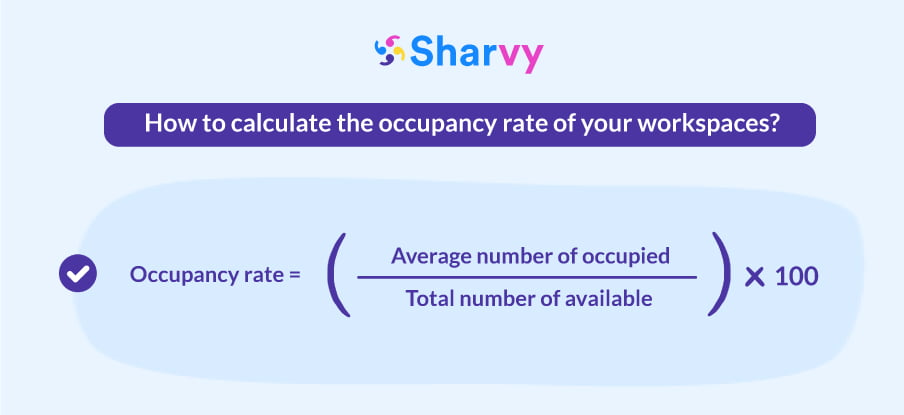
3. Calculate your occupancy rate: divide the average number of occupied stations by the total number of stations available in the company, then multiply by 100 to get a percentage. For example, if you have 100 workstations, and 75 are used on average, your occupancy rate is simply 75%. This helps you understand how your workspaces are being used and optimize them accordingly.
4. Interpret your results: analyze your percentage to understand the efficiency of the use of your workspaces. A high rate (from 80%) indicates a proper use of your workstations, while a low rate (below 70%) may signal underutilized spaces. An occupancy rate between 70% and 80% represents a fairly balanced situation. This means that the majority of your offices & meeting rooms are regularly used, without being overcrowded. You are using your spaces well, but there is still a small margin for improvement!
By following these steps, you will obtain a clear view of the occupancy of your offices, which will help you to adjust the layout, and make the right management decisions, according to YOUR real needs.
So, what are the risks of a too low actual occupancy rate?
No surprise! A too low actual occupancy rate can have negative repercussions on several aspects of your business.
In other words, this means you could be wasting financial resources and precious spaces, which can affect the daily lives of your employees and limit the flexibility of your organization.
Ultimately, in this situation, you end up with:
1. High costs: You are paying for spaces you are not using, which can lead to unnecessary expenses for renting (for example, you rent an entire floor of an office building, but only half is used. Thus, you pay double what is necessary). The same goes for heating, air conditioning, and maintenance (notably, for cleaning that remains constant, even if these spaces are not occupied).
2. Inefficiency of your workspaces: If your offices are empty three-quarters of the time, due to your telecommuting policy, this means that your workspaces are poorly designed and too large compared to your current needs.
3. An impact on the morale of your employees: Empty offices do not contribute to productivity. On the contrary, they can generate a feeling of abandonment and disorganization within the work environment, which can affect the motivation and morale of the employees present. Conversely, a lively work environment promotes collaboration, innovation, and a sense of belonging.
4. Missed opportunities: Empty spaces can be a missed opportunity to host new projects, new teams, and new activities, thus limiting growth and innovation.
You now understand why optimizing workspace has become a top priority for companies looking to find the right balance between resource efficiency and employee satisfaction.
If you would like to discuss optimization strategies on this subject, please do not hesitate to contact us! Our experts will be delighted to answer your questions and discuss your needs (both current and future).
Workplace occupancy rate vs. expansion rate: what are the differences?
The occupancy rate and the expansion rate are two distinct measures concerning the use of workspace. Let’s detail their differences in a few words:
- Occupancy Rate: This measures how many workstations are actually used relative to the total number of available stations. For example, if you have 100 offices and only 60 are used, your occupancy rate is 60%. Therefore, it shows the effective use of your workspaces on a daily basis.
- Expansion Rate: To better understand the difference from the occupancy rate, let’s take an example. Imagine you have 100 offices, but your company allows 150 people to use these offices alternately (for example, some work remotely two to three days a week). Your expansion rate would then be 0.7 (in other words: an average of 7 workstations for every 10 employees), showing that your space can accommodate more people than the number of available offices thanks to flexible and shared use. In other words, the expansion rate assesses the flexibility and hosting capacity of your offices, taking into account variations in use.
✔ What you should remember: The occupancy rate shows the actual use of workstations, while the expansion rate reflects a space’s capacity to adapt to fluctuating needs.
So, should you calculate the occupancy rate of workspaces, or the expansion rate? What strategies to adopt?
Note that it is useful to calculate both the occupancy rate and the expansion rate, BUT be aware, each has a different objective.
- Occupancy Rate: As you understand, it allows you to know how many workstations are (really) used daily, which helps determine if the space is used efficiently, and conversely, if there are surplus offices.
- Expansion Rate: This reveals how many people can use the offices in rotation, even if they are not all present at the same time. It is therefore wise for understanding the flexibility of your workspaces and effectively planning flex office arrangements, as well as your telecommuting policy.
For optimal management, start by calculating the occupancy rate to adjust your spaces according to your current needs. If this rate is low, it may mean that you have too many offices.
Next, calculate your expansion rate to see if you can adopt more flexible solutions, such as flex office and telecommuting, in order to better use the space and offer more flexibility to your employees.
By combining these two measures, you can optimize the use of your offices while meeting the needs of your teams.
Ultimately, what are the benefits of measuring the occupancy rate of your workspaces?
1. Save significantly on costs.
For example, if by calculating your occupancy rate, you find that many of your offices are unoccupied, you could decide to reduce the size of your premises or sublet them. Similarly, if certain areas are only used part-time, you could reduce the frequency of cleaning in these spaces, saving on service costs. Concurrently, having fewer offices to heat and light can significantly reduce your energy bills.
2. Reinvent your workspaces.
By accurately tracking the occupancy and use of your workspaces using tools like Sharvy, you can adapt your spaces to the (real) needs of your employees.
For instance, if they prefer teleworking several days a week, you can adjust your offices for these new habits by creating new spaces. Consider installing more shared workstations and meeting rooms so that they can meet and exchange on various topics when they come to the office. This promotes collaborative work.
3. Improve Quality of Life and Working Conditions (QVCT).
If you find that certain areas are underused, you can redesign these spaces to make them more comfortable and welcoming. For example, transform unused offices into relaxation areas with sofas and plants. This can provide your employees with a place to rest and recharge.
Conversely, if you find that some spaces are often overcrowded, you can reorganize the allocation of your workstations, primarily to work in peace, and to prevent too many people from being in the same area, which reduces noise and stress and makes the work environment more pleasant. This is entirely possible thanks to a dedicated solution like Sharvy.
Discover Sharvy in video for a more explicit explanation of the solution!
Finally, by obtaining various data on the use and occupancy of your workspaces, you can more easily encourage flexible working modes, such as flex office, desk sharing, and telecommuting. For example, if many stations are unoccupied on certain days, your employees can choose to sit wherever they want in the office, according to their needs and preferences.
Ultimately, calculating the occupancy rate of your workspaces helps improve Quality of Life and Working Conditions (QVCT). Notably, because it contributes to creating a more comfortable and flexible environment, increasing the satisfaction of your employees.
In conclusion
At first glance, analyzing and monitoring the occupancy rate of your workspaces may seem technical, but when you look closer and use the right tools, it’s a piece of cake! What’s more, it’s an approach that can bring great benefits.
By tracking the occupancy and use of your various spaces, you can not only optimize your costs but also transform your offices into inspiring and productive environments, featuring welcoming relaxation areas and flexibility that allows everyone to work as they wish.
Thus, it’s not only good for your budget, but it’s also good for the morale and creativity of your teams. So, go for it! Take the time to analyze the occupancy of your spaces and see how a small change can make a big difference.
Have a question ? Check out the FAQ !
What tools can I use to measure the occupation of my workspaces?
There are various tools for measuring the occupation of your workspaces. For example, you can use presence sensors (these are small devices installed on desks and in various meeting rooms, which detect if a workstation is occupied by measuring presence and movement).
Other tools to consider include workstation management software (for example, the Sharvy application), which collects data on reservations and real-time use of workspaces. This type of software can show you how many people are using meeting rooms and at what times, helping you avoid overloads and downtime. Moreover, if your employees reserve desks in advance, you can observe trends and usage peaks.
And more simply, you can choose to conduct surveys among your employees. You ask them how they use the spaces and whether they find the arrangements adequate. This type of survey could reveal whether your employees find that there are too many or too few desks and meeting rooms.
How do the occupancy rate and the expansion rate differ?
The occupancy rate measures the percentage of workstations actually used each day, while the expansion rate indicates how many people can potentially use the workstations in rotation. For example, if you have 100 desks and 70 are used each day, the occupancy rate is 70%. If 150 people share these 100 desks alternately, the expansion rate is 0.7 (that is, an average of 7 workstations for every 10 employees).
What to do if your occupancy rate is too low?
If your occupancy rate is too low, it may indicate an excess of workspace. You can consider reducing the size of your premises, reconfiguring unused spaces, or adopting flexible work practices, such as flex office and telecommuting.
Want to learn more? Check out our latest articles!
Desk Booking : what are the reasons to use it?
What is desk booking? Who is it for? What are the advantages and disadvantages of this practice? Find the answers here.
Hospitality management : the right business strategy?
What is Hospitality Management? Is it the right business strategy? What are the benefits? Focus in this article.
Smart working : the concept that’s revolutionizing the traditional office?
What is smart working? What are its advantages? Why is this concept overturning the traditional office model? The answers in this article.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Resources
Contact us
+44 117 463 6990







